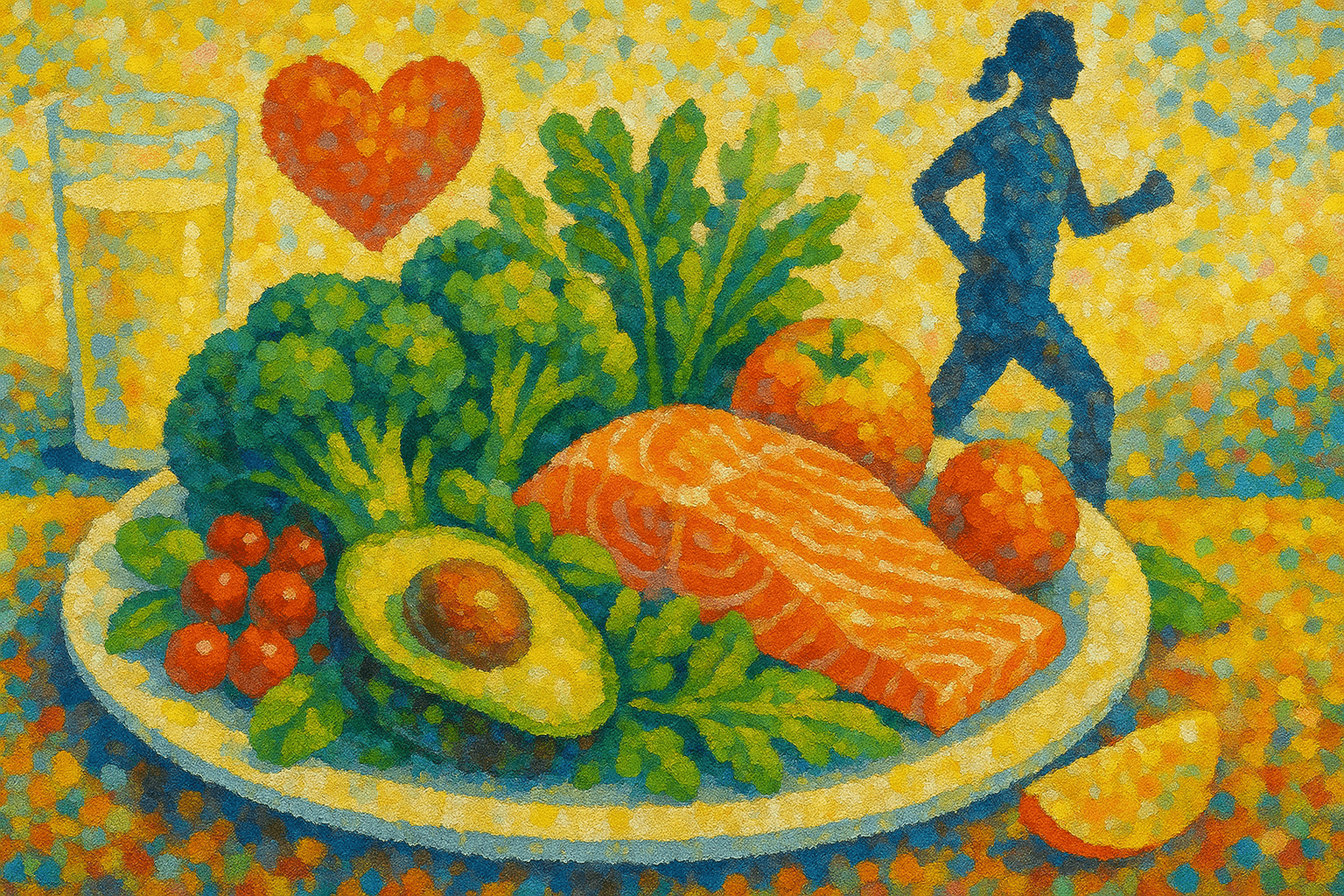Mastering Blood Sugar: The Science and Strategy Behind Better Glucose Control
Published on June 13, 2025

Why Blood Sugar Control Matters
Your body needs glucose for energy, but too much of it over time causes damage. High blood sugar can lead to:
Fatigue and brain fog
Increased hunger and cravings
Belly fat gain
Higher risk of stroke, heart disease, Alzheimer’s
Inflammation and early aging
Mood swings and irritability
Slow wound healing
Even without diabetes, frequent spikes in glucose can contribute to long-term metabolic dysfunction.
Insulin: The Glucose Gatekeeper
Insulin helps glucose move from your bloodstream into your cells. But when your cells stop responding — a condition called insulin resistance — blood sugar stays elevated. Over time, this puts stress on the pancreas and leads to higher fasting glucose.
Surprising Factors That Influence Blood Sugar
Sleep: Just one bad night can raise fasting glucose
Stress: Mental stress can spike glucose as much as sweets
Meal timing: Late-night eating worsens insulin response
Muscle mass: More muscle increases insulin sensitivity
Gut health: A healthy microbiome improves glucose control
The Blood Sugar-Friendly Plate
Skip strict rules. Focus on balance.
1/2 plate non-starchy veggies: spinach, broccoli, peppers
1/4 plate lean protein: chicken, tofu, eggs, fish
1/4 plate complex carbs: sweet potatoes, quinoa, lentils
1–2 tbsp healthy fats: avocado, olive oil, nuts
Add herbs and spices like cinnamon or turmeric to support glucose control. Stay hydrated — even mild dehydration affects glucose metabolism.
Smart Glucose Strategies That Work
Take a Walk After Meals
Just 10–15 minutes can help muscles absorb glucose without insulin.
Front-Load Your Day
Eat larger meals earlier. A protein-rich breakfast supports stable energy.
Prioritize Fiber
25–30g per day from chia seeds, oats, lentils, and veggies slows sugar absorption.
Try Apple Cider Vinegar
1–2 tsp before meals may reduce glucose spikes — ask your doctor first.
Mind Your Meal Order
Eat veggies and protein before carbs to reduce post-meal spikes by up to 30%.
Medication: A Personalized Tool
Some manage blood sugar with lifestyle alone. Others may benefit from medications like metformin or GLP-1 agonists. It’s not failure — it’s personalization. Pair meds with good habits for the best outcome.
Tech Tools to Support You
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) show real-time responses to food
Apps and trackers help identify patterns and encourage movement
Use data for learning and awareness — not punishment
Progress Over Perfection
You don’t need to be perfect. Focus on:
More fiber
More movement
More sleep
Every walk, every balanced meal, every good night’s rest counts. Mastering blood sugar is about living clearer, stronger, and more empowered.
This isn’t just for people with diabetes — it’s for anyone who wants to live better. You’re already on the right path.